Tools
No tools specified.
-
-
Before starting assembly, make sure the jumper wires you plan on using operate properly.
-
Put the multimeter into the continuity mode, which looks like the picture. Also, you need to click the select button once after turning the knob to that setting. You will be able to tell when the solid arrow with a line changes to an open circle and pulses.
-
Then, press one of the prongs onto each side of the wire. If it beeps, that means a signal can travel through and the wire works properly. If no sound is made, get another wire. Keep doing this step until all five jumper wires work properly.
-
-
-
The first thing that needs to be relates to the vibrator. The wires it comes with aren't compatible with any breadboard and will be useless unless we change something. The change that needs to be made is that leads need of solid wire need to be attached to the vibrators leads.
-
The addition of these leads is done by soldering solid core wire to the wires coming off of the vibrator. The amount of solid core wire is based on what you needs are, because the length doesn't affect how the vibrator will operate.
-
After that, heat shrink a case around the two recently soldered wires to protect them. This can be achieved by placing a casing over the wires, and applying heat from a heat gun until the casing shrinks around the wiring.
-
This change will make the vibrator much more stable and easier to connect with the breadboard.The red lead on the vibrator is the positive side where power should flow into, and the black/blue wire is the negative end, where power should flow back to the Ground.
-
-
-
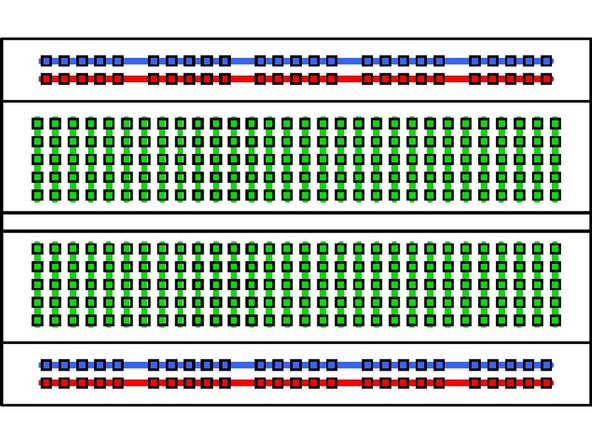
Breadboards are arranged like in the picture. Note the connections like demonstrated in the picture. They are organized in columns when it is set up long ways horizontally, and don't cross over the gap in between.
-
The larger looking breadboard is an actual breadboard that comes with a power line for positive and negative leads. The difference between a mini breadboard and a normal one is the number of columns and the power line.
-
-
-
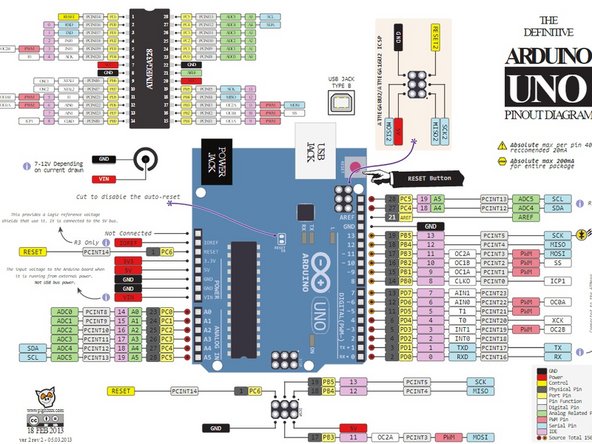
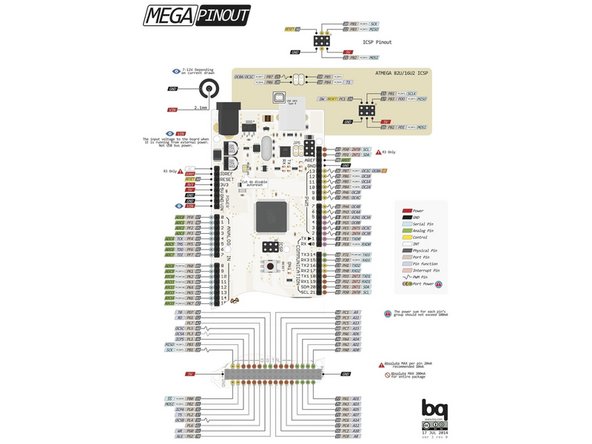
Take the Arduino and plug in a male to male jumper wire in a PWM supported digital pin.
-
For an UNO, it is these pins : 3,5,6,9,10,11
-
For a Mega 2560, it is these pins : 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13
-